Art, as a mirror reflecting the kaleidoscope of human creativity, manifests itself in various styles, each telling a unique story. In this exploration of seven distinct painting styles, we unveil the intricacies that define these artistic movements, accompanied by the brilliance of renowned artists who shaped and defined each genre.
Realism:
Realism emerged in the mid-19th century as a reaction against Romanticism. This style seeks a truthful representation of subjects, emphasizing meticulous details and accurate depictions of everyday life.
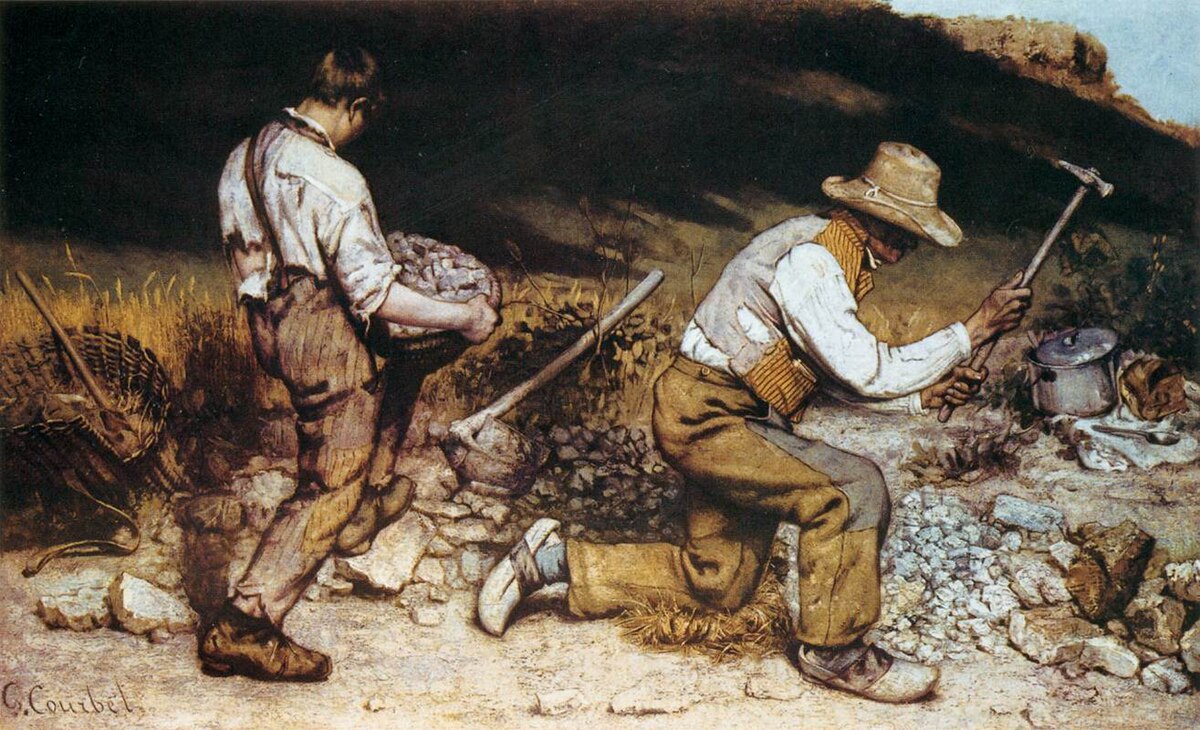

Famous Artist: Gustave Courbet, a leading figure in Realism, crafted works such as "The Stone Breakers" and "A Burial at Ornans," showcasing his commitment to portraying reality without embellishment.
Impressionism:
Impressionism, flourishing in the late 19th century, prioritizes capturing the essence of a scene rather than its precise details. Characterized by loose brushstrokes and an emphasis on light and color, Impressionist paintings often depict outdoor scenes and everyday life.

Famous Artist: Claude Monet, a pioneer of Impressionism, produced masterpieces like "Water Lilies" and "Impression, Sunrise," embodying the movement's focus on capturing the fleeting effects of light.
Abstract Art:
Abstract art, flourishing in the early 20th century, moves away from representational accuracy. It distills visual elements into simplified forms, emphasizing color, shape, and gestural marks to evoke emotions and ideas.

Famous Artist: Wassily Kandinsky, a key figure in abstract art, explored non-representational forms in works like "Composition VII" and "On White II," pioneering a new dimension of artistic expression.
Cubism:
Cubism, initiated by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque in the early 20th century, is characterized by the deconstruction of subjects into geometric shapes. This revolutionary style presents multiple viewpoints simultaneously.
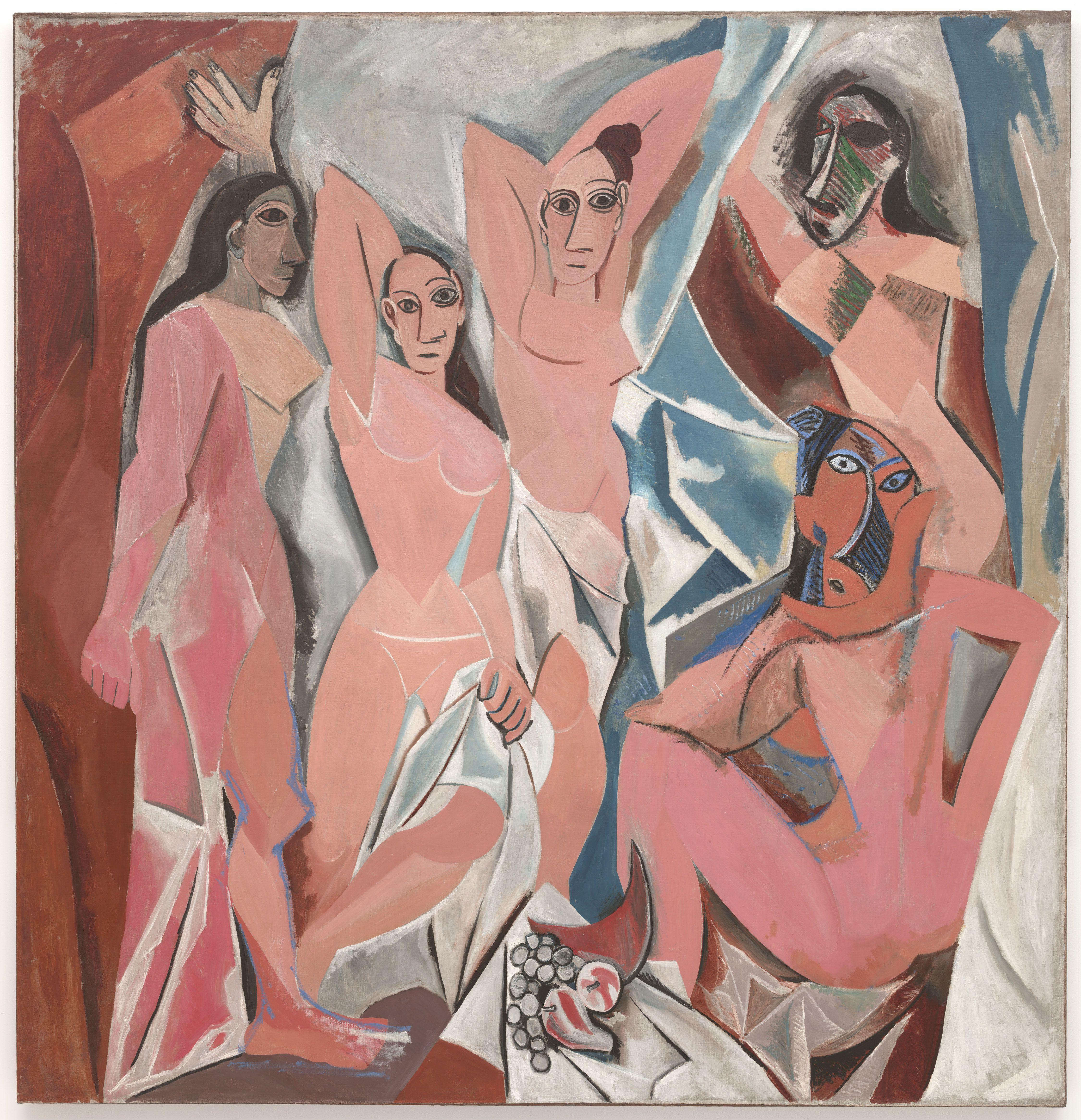

Pablo Picasso, with masterpieces like "Les Demoiselles d'Avignon," and Georges Braque, known for "Violin and Candlestick," co-founded Cubism, challenging traditional perspectives.
Surrealism:
Surrealism, emerging in the early 20th century, explores the realm of the subconscious and dreams. Surrealist paintings often feature fantastical and dreamlike imagery, challenging conventional reality.
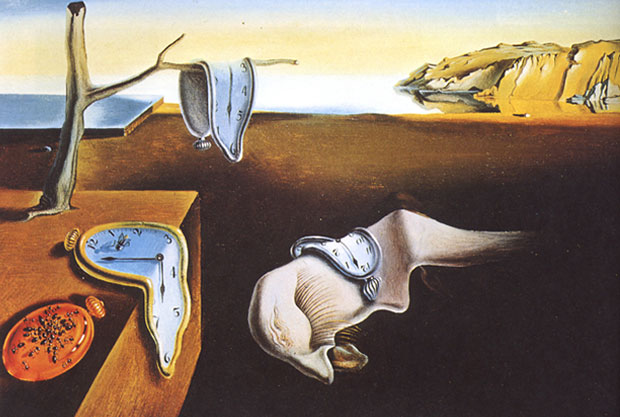
Salvador Dalí, an iconic Surrealist, created surreal masterpieces like "The Persistence of Memory" and "The Elephants," showcasing his vivid imagination and meticulous technique.
Expressionism:
Expressionism, prominent in the early 20th century, emphasizes emotions and subjective experiences over objective reality. This style often employs bold colors, distorted forms, and vigorous brushwork.

Famous Artist: Edvard Munch, renowned for "The Scream," and Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, a key member of German Expressionism, contributed works like "Street, Dresden," embodying the emotional intensity of the movement.
Pop Art:
Pop Art, flourishing in the mid-20th century, incorporates popular culture and mass media imagery into artworks. This style blurs the boundaries between high and low culture, celebrating the everyday.
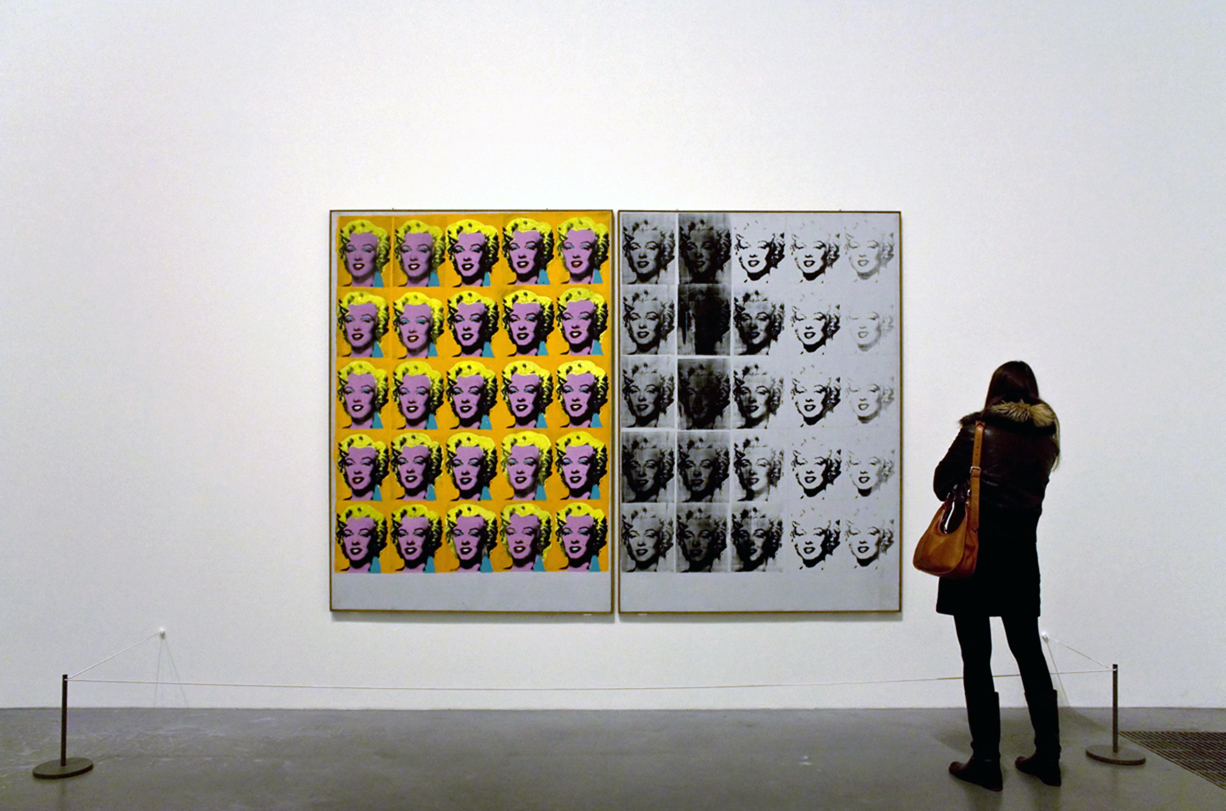

Famous Artist: Andy Warhol, a central figure in Pop Art, created iconic works like "Campbell's Soup Cans" and "Marilyn Diptych," elevating commonplace objects to the realm of high art.
Embark on a visual journey through these seven captivating painting styles, each offering a distinct lens through which artists have interpreted and reshaped the world around them.

